Bridging the Gap: Cross Framework Mapping for AI Governance Controls
Mapping of controls across SOC-2, GDPR, and ISO-42001 can allow efficient implementation of AI governance requirements under the EU AI Act.
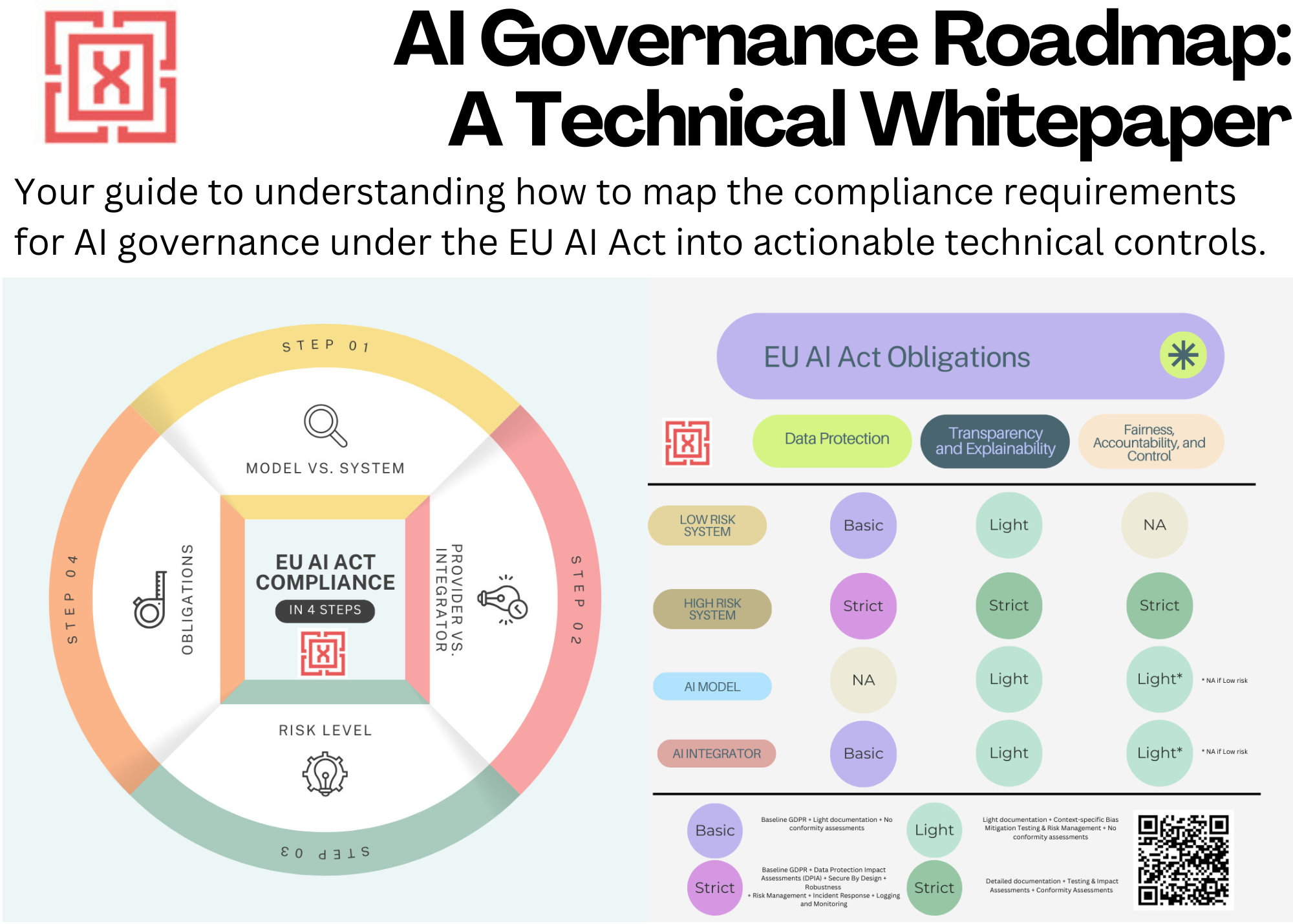
The EU AI Act outlines a set of technical controls based on the risk level of the organization. The challenge for most organizations is to know where to start when faced with these new control requirements introduced under the Act.
Instead of starting from scratch, the process can be made more efficient by leveraging the overlap between the controls that the organization may already have in place based on frameworks such as SOC-2 and GDPR and those required by the frameworks such as ISO-42001 to demonstrate compliance with the Act.
This post will analyze the common controls across these frameworks and provide an approximate coverage that reflects the extent of this overlap. This information can be helpful for organizations to plan their implementation efforts for AI governance.
Cross-Framework Mapping
We begin with a high-level cross-framework mapping that compares controls in SOC-2* and GDPR with those in ISO-42001 aligned with the requirements of the EU AI Act.
*The analysis covers SOC-2 criteria CC & P, for Security & Privacy, respectively.
| AI Governance Domain | EU AI Act Requirement | SOC 2 Alignment | GDPR Alignment | ISO/IEC 42001 Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Management | Art. 9 & 17 – Risk management system | CC3.2, CC9.2 – Risk assessment | Art. 24–25 – 35- DPIAs, risk mitigation | Clause 6.1–6.3 – Risk and opportunity identification |
| Data Governance | Art. 10 – Data quality, relevance, minimization | CC5.0-5.3, CC3.2, CC6.8, CC8.1 – Data handling controls | Art. 5 – Accuracy, data minimization | Clause 6.1, 6.2, 8.2, 8.4 – Data quality and lifecycle control |
| Transparency | Art. 13, 52 – AI system disclosures | CC2.2, 9.2 – Communication of changes, sub-processsors | Art. 12–15, 22 – Transparency obligations | Clause 5.2, 6.2.1, 6.3.1, 8.3, 8.4.4-5 – Explainability and transparency processes |
| Human Oversight | Art. 14 – Human in/on-the-loop controls | CC1.2, CC1.3, CC3.2, CC5.3 – Oversight roles | Art. 22(3), Recital 71 – Right to human intervention | Clause 5.2, 6.1.2, 6.2.1, 8.4.6, 8.5 – Oversight responsibilities and human control |
| Security & Resilience | Art. 15 – Robustness, cybersecurity | CC6.1-8, CC7.1-5 – Logical and physical security | Art. 32, Rectials 39, 83 – Security of processing | Clause 6.1.2, 8.2.2, 8.4.2, 8.4.8 – Security and resilience in AI operations |
| Logging & Traceability | Art. 12 – Automatic logs of system activity | CC6.6, CC7.2 – Audit logs | Art. 5(2), 30, 33-34 – Record of processing activities | Clause 6.1.2, 8.2.2, 8.4.7, 8.6, 9.1– Logging, monitoring, and post-deployment traceability |
| Data Subject Rights | Art. 5, 52, 68, 84 – Interaction, access, and explanation rights | P3.1-3.6, P4.1-2, P6.1-2 – User request handling | Art. 12–23 – Access, erasure, objection | Clause 5.2-3, 6.1.3, 6.2.2, 8.4.1, 8.4.4 – User communication and rights handling |
| Incident & Post-Market Monitoring | Art. 23, 61, 62, 67, 84 – Monitoring and reporting failures | CC3.2, CC7.2-5, CC9.2-4, P6.2 – Monitoring, remediation | Art. 24, 32-35 – Risk monitoring and breach notification | Clause 9.1, 10.2 – Incident tracking and continual improvement |
| Accountability & Roles | Art. 4, 16–29, 61 – Role of provider, deployer, importer, distributor | CC1.2-3, CC2.2, CC5.3 – Governance & accountability | Art. 5(2), 24-28, 30, 32, 35 – Controller and processor roles, Security measures, DPIA | Clause 5.1–5.3, 6.1.3, 8.4.1-5 – Leadership, responsibilities, accountability |
| Lifecycle Management | Art. 9–15, 61 – Technical documentation, updates | CC5.1-2, CC6.1-2, CC7.1, 8.1 – Change management | Art. 5(1), 25, 30, 35 – Documentation of processing, DPIA | Clause 6.1.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.5.2 – AI lifecycle and documentation |
Domain-Level Breakdown
We will now break this down further into individual domain-level controls. For each domain, we will provide a coverage score, which indicates the extent of overlap between existing controls and those required under the EU AI Act.
A coverage score of X would mean that an organization that has implemented SOC-2 and GDPR controls will have X% coverage for the corresponding controls required by ISO-42001 to demonstrate compliance with the EU AI Act.
[A ✅ counts as 1, ⚠️ as 0.5, and ❌ as 0 toward the coverage score.]
Risk Management
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formal Risk Management Process | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Lifecycle Risk Monitoring | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| AI-Specific Risk Criteria | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Accountability Framework | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Post-Deployment Risk Updates | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
Data Governance
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy & Completeness | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Data Documentation & Traceability | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Bias/Fairness Mitigation | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| AI-Specific Dataset Governance | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
| Lifecycle Integration | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
Transparency
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User-Facing Transparency | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Model Explainability | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| System Documentation | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| AI Interaction Disclosure | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Communication of Limitations | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
Human Oversight
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human-in-the-loop Oversight | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Right to Manual Override | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Documentation of Oversight | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Risk-Based Oversight Implementation | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
| Operational Mechanisms for Intervention | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
Security & Resilience
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System Security | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Threat Detection & Monitoring | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Adversarial Attack Mitigation | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
| System Resilience & Fault Tolerance | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| AI-Specific Risk Modeling & Controls | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
Logging & Traceability
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logging of Operations | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Auditability of AI Decisions | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
| Model Lifecycle Traceability | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
| Logging for Compliance Demonstration | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Incident & Breach Logging | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
Data Subject Rights
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right to Access / Correction | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Right to Deletion / Objection | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Transparent AI Decision Use | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Human Override / Avoid Automation | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Redress / Complaint Mechanisms | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
Incident & Post-Market Monitoring
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Monitoring Post-Deployment | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Incident Detection and Logging | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Regulatory / Authority Reporting | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Trend & Root Cause Analysis | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Process Improvement Based on Incidents | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
Accountability & Roles
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Role-Based Obligations | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Defined Responsibilities for Compliance | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Assignment of Internal Oversight | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Contractual / Legal Accountability | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Continuous Responsibility in Lifecycle | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
Lifecycle Management
| Capability | EU AI Act | SOC 2 | GDPR | ISO/IEC 42001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full AI Lifecycle Coverage | ✅ | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ✅✅ |
| Design/Development Risk Controls | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Post-Deployment Feedback Integration | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Change Management During Lifecycle | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| Formal Decommissioning Guidance | ⚠️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅✅ |
Key Observations
Based on the above cross-framework mapping and domain-level breakdown, its helpful to note the following observations:
- Out of the 10 categories, the coverage based on existing controls ranges from high (> 75% ) for 2 of them, to medium (50-75%) for 5 of them, and to low (< 50%) for 3 of them.
- SOC 2 contributes strong operational controls, —but lacks AI-specific provisions like bias mitigation or human oversight.
- GDPR aligns closely with the data governance and individual rights aspects of the EU AI Act.
- ISO/IEC 42001 is the most AI-specific standard, directly supporting structured implementation of EU AI Act requirements across the entire lifecycle, from design to monitoring.
Conclusion
This post analyzed the common controls across SOC-2, GDPR, and ISO-42001 aligned with the EU AI Act, and provided a coverage score for the various control categories to indicate the extent of overlap between them. This information can be helpful for organizations to plan their implementation efforts for AI governance.
Sign up to receive a copy of our AI Governance Roadmap.
Connect with us
If you would like to reach out for guidance or provide other input, please do not hesitate to contact us.